What is QOS ?
Quoting site wikipedia.org
Definitions:
---------------------*
In the field of telephony, quality of service was defined by the ITU in 1994.[1] Quality of service comprises requirements on all the aspects of a connection, such as service response time, loss, signal-to-noise ratio, cross-talk, echo, interrupts, frequency response, loudness levels, and so on. A subset of telephony QoS is grade of service (GoS) requirements, which comprises aspects of a connection relating to capacity and coverage of a network, for example guaranteed maximum blocking probability and outage probability.[2]
/ip firewall mangle
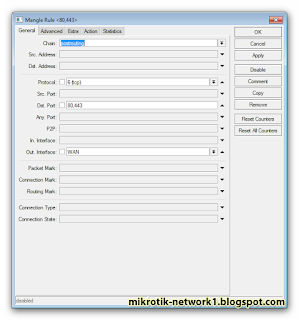
add action=mark-packet chain=postrouting out-interface=WAN passthrough=no new-packet-mark=QoS_1_Up dst-port=80,443 packet-size=0-666 protocol=tcp tcp-flags=syn comment=QoS
add action=mark-packet chain=postrouting out-interface=WAN passthrough=no new-packet-mark=QoS_1_Up dst-port=80,443 packet-size=0-123 protocol=tcp tcp-flags=ack
add action=mark-packet chain=postrouting out-interface=WAN passthrough=no new-packet-mark=QoS_1_Up dst-port=53,123 protocol=udp
add action=mark-packet chain=postrouting out-interface=WAN passthrough=no new-packet-mark=QoS_2_Up dst-port=80,443 connection-bytes=0-1000000 protocol=tcp
add action=mark-packet chain=postrouting out-interface=WAN passthrough=no new-packet-mark=QoS_2_Up dst-port=110,995,143,993,25,20,21 packet-size=0-666 protocol=tcp tcp-flags=syn
add action=mark-packet chain=postrouting out-interface=WAN passthrough=no new-packet-mark=QoS_2_Up dst-port=110,995,143,993,25,20,21 packet-size=0-123 protocol=tcp tcp-flags=ack
add action=mark-packet chain=postrouting out-interface=WAN passthrough=no new-packet-mark=QoS_3_Up packet-size=0-666 protocol=tcp tcp-flags=syn
add action=mark-packet chain=postrouting out-interface=WAN passthrough=no new-packet-mark=QoS_3_Up packet-size=0-123 protocol=tcp tcp-flags=ack
add action=mark-packet chain=postrouting out-interface=WAN passthrough=no new-packet-mark=QoS_4_Up dst-port=110,995,143,993,25,20,21 protocol=tcp
add action=mark-packet chain=postrouting out-interface=WAN passthrough=no new-packet-mark=QoS_4_Up dst-port=80,443 connection-bytes=1000000-0 protocol=tcp
add action=mark-packet chain=postrouting out-interface=WAN passthrough=no new-packet-mark=QoS_8_Up p2p=all-p2p
add action=mark-packet chain=postrouting out-interface=WAN passthrough=no new-packet-mark=QoS_7_Up
add action=mark-packet chain=postrouting out-interface=WAN passthrough=no new-packet-mark=QoS_2_Up src-port=8291 comment=WinBox
/queue tree
add max-limit=666K name=QoS_WAN_Up parent=WAN
add name=QoS_1 packet-mark=QoS_1_Up parent=QoS_WAN_Up priority=1
add name=QoS_2 packet-mark=QoS_2_Up parent=QoS_WAN_Up priority=2
add name=QoS_3 packet-mark=QoS_3_Up parent=QoS_WAN_Up priority=3
add name=QoS_7 packet-mark=QoS_7_Up parent=QoS_WAN_Up priority=7
add name=QoS_8 packet-mark=QoS_8_Up parent=QoS_WAN_Up priority=8
add name=QoS_4 packet-mark=QoS_4_Up parent=QoS_WAN_Up priority=4
See you in the next lesson
Quoting site wikipedia.org
Definitions:
---------------------*
In the field of telephony, quality of service was defined by the ITU in 1994.[1] Quality of service comprises requirements on all the aspects of a connection, such as service response time, loss, signal-to-noise ratio, cross-talk, echo, interrupts, frequency response, loudness levels, and so on. A subset of telephony QoS is grade of service (GoS) requirements, which comprises aspects of a connection relating to capacity and coverage of a network, for example guaranteed maximum blocking probability and outage probability.[2]
In the field of computer networking and other packet-switched telecommunication networks, the traffic engineering term refers to resource reservation control mechanisms rather than the achieved service quality. Quality of service is the ability to provide different priority to different applications, users, or data flows, or to guarantee a certain level of performance to a data flow. For example, a required bit rate, delay, jitter, packet dropping probability and/or bit error rate may be guaranteed. Quality of service guarantees are important if the network capacity is insufficient, especially for real-time streaming multimedia applications such as voice over IP, online games and IP-TV, since these often require fixed bit rate and are delay sensitive, and in networks where the capacity is a limited resource, for example in cellular data communication.
A network or protocol that supports QoS may agree on a traffic contract with the application software and reserve capacity in the network nodes, for example during a session establishment phase. During the session it may monitor the achieved level of performance, for example the data rate and delay, and dynamically control scheduling priorities in the network nodes. It may release the reserved capacity during a tear down phase.
A best-effort network or service does not support quality of service. An alternative to complex QoS control mechanisms is to provide high quality communication over a best-effort network by over-provisioning the capacity so that it is sufficient for the expected peak traffic load. The resulting absence of network congestion eliminates the need for QoS mechanisms.
QoS is sometimes used as a quality measure, with many alternative definitions, rather than referring to the ability to reserve resources. Quality of service sometimes refers to the level of quality of service, i.e. the guaranteed service quality. High QoS is often confused with a high level of performance or achieved service quality, for example high bit rate, low latency and low bit error probability.
An alternative and disputable definition of QoS, used especially in application layer services such as telephony and streaming video, is requirements on a metric that reflects or predicts the subjectively experienced quality. In this context, QoS is the acceptable cumulative effect on subscriber satisfaction of all imperfections affecting the service. Other terms with similar meaning are the quality of experience (QoE) subjective business concept, the required “user perceived performance”,[3] the required “degree of satisfaction of the user” or the targeted “number of happy customers”. Examples of measures and measurement methods are Mean Opinion Score (MOS), Perceptual Speech Quality Measure (PSQM) and Perceptual Evaluation of Video Quality (PEVQ). See also subjective video quality.
----------------------*
How to Activation of the quality of services in the server Mikrotik (QOS) ?
Follow ME
Lesson today speaks of the quality of services in the server
(QOS)
This service exists in the server Mikrotik Let's not active
We will activate the service by placing the following rolls
#Name card access to the Internet WAN
#Change it in the script to the name of your card
#Change the overall speed of the line
max-limit=.... Your Speed
#Name card access to the Internet WAN
#Change it in the script to the name of your card
#Change the overall speed of the line
max-limit=.... Your Speed
/ip firewall mangle
add action=mark-packet chain=postrouting out-interface=WAN passthrough=no new-packet-mark=QoS_1_Up dst-port=80,443 packet-size=0-666 protocol=tcp tcp-flags=syn comment=QoS
add action=mark-packet chain=postrouting out-interface=WAN passthrough=no new-packet-mark=QoS_1_Up dst-port=80,443 packet-size=0-123 protocol=tcp tcp-flags=ack
add action=mark-packet chain=postrouting out-interface=WAN passthrough=no new-packet-mark=QoS_1_Up dst-port=53,123 protocol=udp
add action=mark-packet chain=postrouting out-interface=WAN passthrough=no new-packet-mark=QoS_2_Up dst-port=80,443 connection-bytes=0-1000000 protocol=tcp
add action=mark-packet chain=postrouting out-interface=WAN passthrough=no new-packet-mark=QoS_2_Up dst-port=110,995,143,993,25,20,21 packet-size=0-666 protocol=tcp tcp-flags=syn
add action=mark-packet chain=postrouting out-interface=WAN passthrough=no new-packet-mark=QoS_2_Up dst-port=110,995,143,993,25,20,21 packet-size=0-123 protocol=tcp tcp-flags=ack
add action=mark-packet chain=postrouting out-interface=WAN passthrough=no new-packet-mark=QoS_3_Up packet-size=0-666 protocol=tcp tcp-flags=syn
add action=mark-packet chain=postrouting out-interface=WAN passthrough=no new-packet-mark=QoS_3_Up packet-size=0-123 protocol=tcp tcp-flags=ack
add action=mark-packet chain=postrouting out-interface=WAN passthrough=no new-packet-mark=QoS_4_Up dst-port=110,995,143,993,25,20,21 protocol=tcp
add action=mark-packet chain=postrouting out-interface=WAN passthrough=no new-packet-mark=QoS_4_Up dst-port=80,443 connection-bytes=1000000-0 protocol=tcp
add action=mark-packet chain=postrouting out-interface=WAN passthrough=no new-packet-mark=QoS_8_Up p2p=all-p2p
add action=mark-packet chain=postrouting out-interface=WAN passthrough=no new-packet-mark=QoS_7_Up
add action=mark-packet chain=postrouting out-interface=WAN passthrough=no new-packet-mark=QoS_2_Up src-port=8291 comment=WinBox
/queue tree
add max-limit=666K name=QoS_WAN_Up parent=WAN
add name=QoS_1 packet-mark=QoS_1_Up parent=QoS_WAN_Up priority=1
add name=QoS_2 packet-mark=QoS_2_Up parent=QoS_WAN_Up priority=2
add name=QoS_3 packet-mark=QoS_3_Up parent=QoS_WAN_Up priority=3
add name=QoS_7 packet-mark=QoS_7_Up parent=QoS_WAN_Up priority=7
add name=QoS_8 packet-mark=QoS_8_Up parent=QoS_WAN_Up priority=8
add name=QoS_4 packet-mark=QoS_4_Up parent=QoS_WAN_Up priority=4
The result after adding rolls
See you in the next lesson
with you
Mohamed samir

























































Where is priority 5?
ReplyDelete